ASCE 7-16 Wind Changes

The ASCE 7-16 Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures was released in the Summer of 2017, and some jurisdictions are starting to reference this standard. MecaStack has a built in calculator for ASCE 7 wind loads on the stack, but Meca also offers a program called MecaWind which calculates wind loads on any type of structure per ASCE 7-05 / 10 / 16. In the course of updating MecaWind to include ASCE 7-16, we have become quite familiar with the ASCE 7-16 standard and wanted to summarize some of the major changes.
Summary of ASCE 7-16 Changes:
The new ASCE 7-16 standard offered many changes to the ASCE 7-10. MecaWind includes ASCE 7-05, ASCE 7-10 and ASCE 7-16, and includes all of the changes in the new standard. I wanted to take a minute to explain some of the major changes that occurred in ASCE 7-16.
- Addition of a new Classification: “Partially Open Building”
- Wind Maps for Hawaiian Islands added
- New Wind map for Risk Category IV added
- Wind Speeds in non-hurricane regions decreased, and contours in Northeast USA revised
- Now a new parameter “Ke” added to account for reduced wind pressures at higher altitudes.
- Edge zone side dimension ‘a’ has been reduced for very large buildings with low sloped roofs.
- Transverse Frame criteria has been added
- Criteria for Rooftop Equipment has been revised and expanded
- Significant changes for Bins, Silos and Tanks
- Solar Panel criteria for Rooftop mounted panels added
- Flat and Sloped Roofs <= 60 ft saw an increase in component and cladding pressures; however, for h < 30 ft in Exposure B also saw some reductions.
- Gabled & Hipped Roofs <= 60 ft have significantly revised figures for Components and Cladding pressures that cover a wider range of slopes.
- Criteria on loads on Canopies has been added
- Components and Cladding Ch 30 Pt 2 completely revised the tables.
- Components and Cladding Ch 30 Pt 4 now refers to Ch 30 Pt 2 when h <= 60 ft.
Although most of these changes are not relevant to stacks, we have incorporated all of these changes into our MecaWind software.
How does ASCE 7-16 Change for Stacks:
MecaStack includes the comprehensive stack design code ASME STS-1 ‘Steel Stack Design’. In this standard, the ASCE 7-05 wind load calculations are used, which were based upon an Allowable Stress Wind Speed. Recently the ASME STS-1 standard was revised to allow Ultimate Wind Speeds to be entered per ASCE 7-10. The revision was made by simply converting the ASCE 7-10 Wind Speed (Ultimate) to an equivalent ASCE 7-05 Wind Speed (Allowable). From that point on the calculations are the same as they would have been using ASCE 7-05. The STS committee has not yet determined what they will do with ASCE 7-16, but it seems that eventually the committee will have to revise the STS standard to use Ultimate wind speeds, since that is going to the basis for ASCE 7 from now on it appears.
There aren’t many changes in ASCE 7-16 that impact stacks. There are some revisions to the wind maps, and there is the possibility to consider a reduction in wind pressures at higher altitudes due to the air being less dense. It is unclear if STS will allow for this reduction within the Stack code.
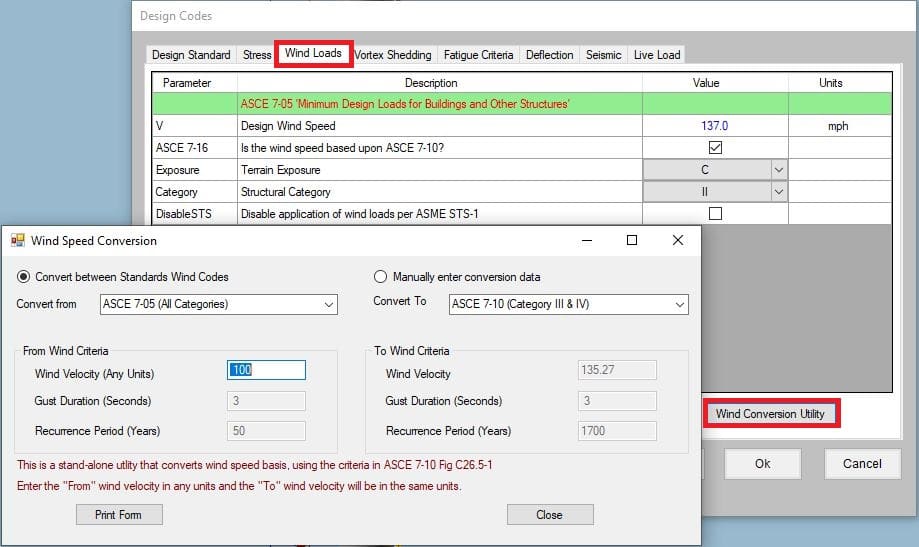
Wind Conversion Utility
MecaStack has a Wind Conversion Utility which few users know about It’s found by going to the Design Code menu, and then select Wind Code and then Click the Wind Conversion Utility button. You select the original code on the left, and then select the code you are converting to on the right.